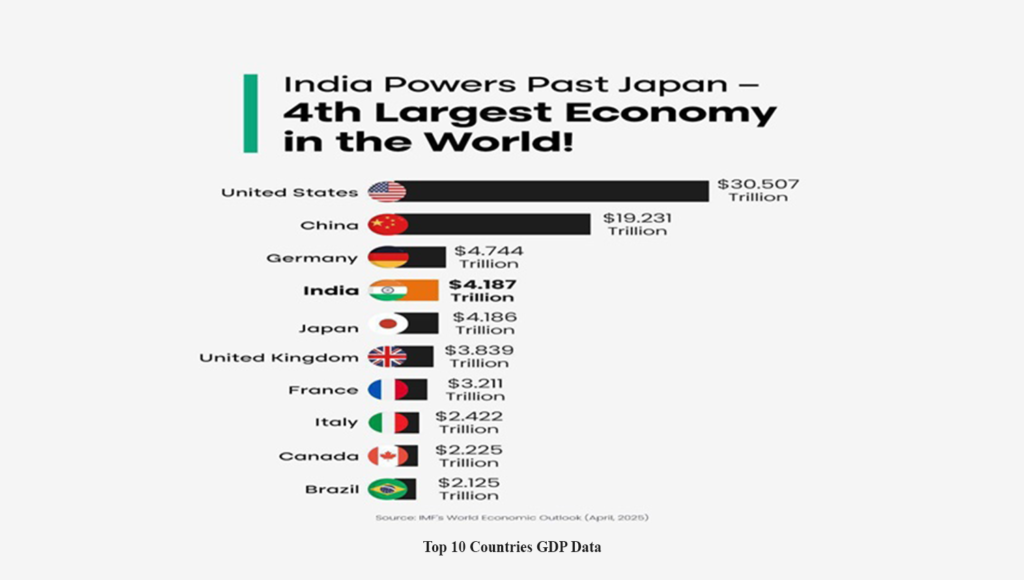
India has officially surpassed Japan to become the fourth-largest economy in the world, in terms of nominal GDP. This is a significant change in the global economic landscape. The April edition of the World Economic Outlook report by IMF stated that the nominal GDP for fiscal 2026 is estimated to reach $4,187.017 billion which is marginally higher than the GDP of Japan at $4,186.431 billion. India now stands behind only the United States, China, and Germany. This recent achievement shows India’s sustained economic growth, driven by robust domestic demand, rising digital adoption, and strategic policy reforms. Major sectors like services, manufacturing, and infrastructure have an important role in fueling growth, and production-linked incentive (PLI) schemes and improvements in the digital economy have attracted global investment.
In contrast, Stagnation and demographic headwinds create obstacles for Japan’s economy. Multiple factors affect Japan’s long-term prospects, such as an aging population, a shrinking workforce, and deflationary pressures. India continued its economic expansion, while Japan’s nominal GDP has plateau around $4-5 trillion.
This major achievement has significant implications for investment, global trade, and geopolitics. After becoming the fourth-largest economy at the global level, India is in stronger position to define global policies, attract capital, and reshape its role in global supply chains. Surpassing Japan is a new chapter in India’s economic growth but to maintain its trajectory India must need to address infrastructure gaps, income inequality, and regulatory hurdles.
Factors behind Economic rise
India’s improvement in global GDP ranking is not an overnight action. Reaching this position at the global level is a result of deep-rooted structural changes and long-term economic strategies that positioned the country as one of the fastest-growing economies in the world. These three factors stand out for economic expansion.
-
Demographic
India’s current population is more than 1.4 billion and the majority of people are young. With an average age of under 30, India has the youngest workforce globally. It gives an important advantage in terms of labor supply, consumer demand, and productivity potential. On the contrary, major advanced economies face an aging population and falling labor forces. The young population of India fuels consumption, and support sectors like retail, technology, housing, and education which sustain domestic demand. This favorable demographic change provides India an opportunity to build a competitive labor-intensive manufacturing base and vibrant digital service sector.
India needs to fully utilize the capabilities of this young workforce. It is important for India to carry on investing in skills development, healthcare, education, and employment generation- ensuring the right capitalization of the young population.
-
Economic reforms
The structural reforms implemented over the past decade have significantly transformed the Indian economic landscape. With the help of these reforms, the Indian economy enhances its transparency, improves tax compliance, modernizes the economy, and promotes ease of doing business. Implementation of GST (Goods & Service Tax) is one of the most significant changes that replaced multiple state & central taxes and created a unified tax system. GST helps reduce tax inefficiencies, simplifies logistics, and increases formalization across industries.
Another game changer is the Unified Payment Interface (UPI) which gives a major positive shift in digital payments. UPI helps foster financial inclusion and reduces the cash dependency of small businesses and consumers which made India a global leader in digital transactions.
The launch of Production-Linked Incentives (PLI) schemes in multiple sectors such as electronics, semiconductors, and pharmaceuticals has attracted global manufacturing companies by offering incentives tied to output. The aim of these policies is to position India as a global manufacturing hub and reduce dependency on imports. Together, all these reforms at the economic level built a resilient, inclusive, and competitive economic foundation.
-
Global diversification
The rise of India at the global level is also tied to changing global supply chain dynamics. Many multinational companies have adopted the “China+1” strategy for diversifying their manufacturing units from China and this worked in favor of India. There are multiple factors like rising geopolitical tensions, labor costs, and disruption in the supply chain during the pandemic have played significant roles in considering India as a viable alternative for global firms. India provides a large domestic market, improving infrastructure, and a vast number of technical and engineering talents.
The Indian government has changed its policies to take advantage of the situation with investor-friendly policies, fast-tracking approvals, and efforts to improve infrastructure. It includes making industrial corridors and port modernization which make India more competitive in global manufacturing.
Impact on Global Economy
Rapid economic rise for India’s economy is reshaping the global scenario, carrying various implications for trade, geopolitics, investment, and global governance. The rise in India’s GDP provides greater weight in international decision-making bodies such as the IMF, WTO, and G20. It gives a better position for India to affect global economic policies, stand for the interest of emerging markets, and reshape rules of global trade and finance. India is becoming a top choice for foreign direct investment (FDI), from an investment perspective. With an improving infrastructure, large consumer base, and digital adoption at a vast scale, offers a better option for investors seeking a better growth market as compared to western saturated markets.
There is a significant change in global trade and investment flows towards South Asia, and India emerges as a center of this investment. The role of India in the “China+1” strategy is crucial because it diversifies supply chains and reduces China’s dependency. These new changes give a strong position of India in global manufacturing and technological ecosystems.
Upcoming Challenges
The rise of the Indian economy is impressive but to sustain this momentum will require resolving some serious problems that could shape its journey. The most important concern for the Indian economy is persistent income inequality and uneven regional development. Urban centers and industrial states have seen some growth but large parts of rural Indian states are still lagging behind. Filling this gap is important for better growth and long-term economic stability. India also faces notable infrastructure, healthcare, and educational gaps. Although improvement have been made in this area such as addressing congested port development and providing quality education and basic healthcare. Expanding and modernizing infrastructure, healthcare, and education are essential for building resilient and robust economic growth.