NSE Option Chain Analysis: How It Works & What Does Indicate
In the stock market, apart from cash trading, there is another segment called derivatives where a huge volume of trades take place every day. Under the derivatives segment, Futures & Options are the value of cash market underlying stocks or indices. The "Option Chain" – is the word derived from here where it is widely used by traders to understand stocks.
What is Option Chain?
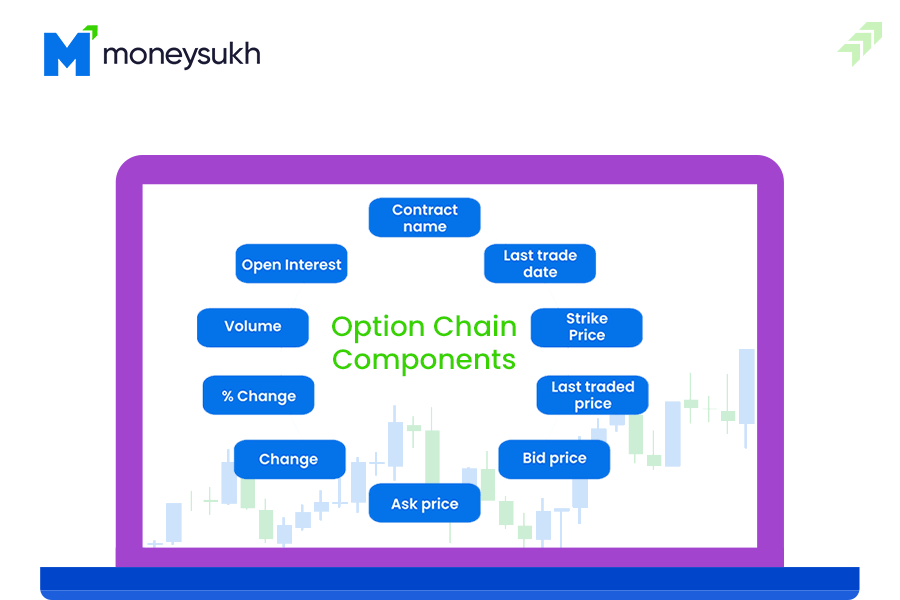
An option chain is a kind of option matrix showing the list of all contracts of an index or stock of any company. Option chain shows the calls and puts listed on the exchange with other details like the contract expiration date, strike price, volume, open interest and the last trading price of the underlying security or index with the maturity period of that contract.
Call and Put two types of options contracts are listed there, in which the call option gives you the right but not the obligation to buy for the underlying stock at a specified price and within the expiration date of that option. While on the other hand, the put option is a contract that gives you the right but not the obligation to sell the underlying stock at a specified price and within the expiration date of that option contract.
To read the option chain you need to understand its other components, and what and how each of the components shows the accumulated information of underlying stock. It simply provides detailed price information for each underlying stock on NSE.
How Option Chain Works?
The option chain works simply as per the price movement in the underlying stock or index. When the market starts with the number of trades the details of the option chain keep changing. And traders make their decisions according to the option price movement.
Also Read: Options Trading for Beginners
Call and Put options change with the change in the current market price of the stock. All other components are affected by the price and OI change. So before we move further let’s know about all the other components of the option chain.
Option Chain Analysis:

Strike Price: This is the price at which the buyer and seller of an option agreement exercise the contract. And when the price exceeds this strike price the option contract becomes profitable.
Last Trade Price: This is the price last time traded on the exchange and this LTP changes during market hours as per the change in the cash market price of the stock or index.
Ask Price: The asking price is the lowest price of the stock at which the seller of the stock is ready to sell the quoted security. Mostly the lowest ask price of any stock is quoted in the stock market for trading.
Bid Price: This is the highest price of the stock at which the buyer is ready to buy quoted stocks. This is the best market price a trader is ready to buy.
Bid Quantity: This is the quantity buyer is ready to buy the number of stocks at a specific strike price It is the latest demand for the strike price of an option.
Ask Quantity: It is the quantity seller is ready to sell the number quantity of stocks at a specific strike price. It is the availability of the option.
In-the-Money: When the strike price of a call option is smaller than the present market value then this option is called an in-the-money option. Conversely, when the strike price is greater than the current market price the option is called in-the-money.
Out-of-the-money: When a call option's strike price is greater than the current market price of the underlying asset, then the option is out of the money. Similarly, in a put option, when the strike price is less than the current market price of an underlying stock, then it is considered an out-of-money option.
At-the-money: When the strike price of a call or put option is equal to the strike price of the market price of the underlying asset then it is called the at-the-money.
Open Interest (OI): Open interest generally shows the interest of the traders during a specific strike price that is visible through the open positions for a particular contract that is not yet closed or expired or not yet exercised.
Change in OI: It is the change in the open interest before the date of expiry of the contract. And the difference between the OI shows that either the contract is expired, closed, squared off or exercised by either party (buyer & seller).
Volume: The volume in the option chain is the number of contracts traded in the market for the particular strike price contract. The volume shows the liquidity in the market and helps to understand the current interest of the traders.
Implied Volatility: Implied volatility shows the swing of the price of the option chain. Higher implied volatility means a high swing in the price, while low implied volatility means a low swing in the price. This generally shows the volatility of call or put options.
Also Read: VIX India: How it Works, Calculated & Used for Share Trading
How to Read Option Chain Data in NSE?
Once you got know about the above-listed terminologies it would be easier to read and understand the Option chain data. When you see the matrix of the option chain of any stock or underlying index you see the data with different headings like security name, symbol strike price, last trade price, price change, bid, ask, volume, and open interest etc.
Types of Options: Stock exchanges or brokers show the option chain data or real-time or delayed data. Traders can choose any of the strike price calls or put options to make the position. A call option is a contract that gives you the right to but not the obligation to buy any underlying security at the specified price within the expiry date of the option.
While on the other hand, the Put option is the contract that gives you the right but the obligation to sell an underlying security at a specified price but within the expiry date of the option contract.
If you are exploring the option chain at NSE, you can click on any strike price and check all the details like price, OI, volume, change in price and OI etc. You can also check these details through contract wise for different weeks, months or years.
What Does Option Chain Indicate?
The option chain matrix consists of various details showing the trend towards that stock or index. The change in open interest with the price change shows it is going to move in the upcoming days. Though various factors affect the price of a call or put option as soon as the expiration date of the contract nearing to end the price changes accordingly.
Basically, the option chain indicates how the sentiments of the traders towards a particular stock. When you analyze the correlation between the change in OI and the change in the price of the underlying security, it indicates the stock is expected to move on either side. To understand better how price changes and OI changes correlate with others you have to read about open interest and its other dynamics separately in another article that will available on our website.
Also Read: Short straddle and strangle option strategy
Nifty Option Chain
The Nifty option chain is the matrix of all active call and put options of the Nifty 50 index. In Nifty Option Chain, you can see all the active calls and puts of the different strike prices. You can filter the Nifty 50 Option Chain contract-wise for a different month, year or week.

Image source: nseindia
You can also use the combination of the NSE Option chain of the different strike prices. And if you want to see all the contracts of particular strike price you can click on the link given on the strike price. However, when you open the Nifty Option Chain, by default it shows all the calls and put options of the nearest expiration month with the option to choose anyone.
Also Read: VIX India
Bank Nifty Option Chain
Similarly, the Bank Nifty option chain is listed on the NSE, where you can see all the call and put options of the different strike prices of the nearest month. Here again, you can choose the strike price to see all the contracts of different months actively trading.
Bank Nifty Options Chain is the underlying index of all the banks included in the Bank Nifty Index. It shows how all these banks perform and traders make their options as per the market trend. Similarly, there are other indices where the option chain is listed.
Summing-up
Before closing this key discussion about option chains, I would like to say, if you are dealing with a cash market option chain analysis would be not difficult for you. And then becoming aware of all the components of the option chain and how to read or analyses them, it becomes easier to understand how the option chain works in real-time in the market.
Though, we already told you there is a significant relationship between option chain price change and change in the open interest. Once you understand that you will get to know how to use the option chain to analyse the market sentiments. And traders use these option chains to form strategies to maximize profits and minimize their loss in the market.
Frequently Ask Questions (FAQs) – Option Chain & Trading
Q1. What is Call Option?
Ans. CALL Option means when someone buys the right to buy (but not the obligation) a security or stock at a specified price within a specific period in future. The underlying security can be any financial instrument trading in the future and options market like stocks, bonds and commodities.
Q2. What is Put Option?
Ans. PUT Option is a contract that gives the option buyer a right (but not obligation) to sell the specific quantity of underlying security at a predetermined price at a specified date in future. Put options can be also used to trade different types of underlying assets, such as stocks, commodities, bonds and currencies.
Q3. What is European Option?
Ans. A European option is a type of option contract, that can be exercised only on the date of exercise or you can say expiration day. Mean option contract holders cannot exercise the option before the date of the exercise date. In the European option, both Call & Put actions can take place on the date of maturity of the option.
Q4. What is American Option?
Ans. In American Option, an option holder can exercise their right option contract any time before including the date of contract expiration. This means an American option can be exercised both before and on the maturity date.
Q5. What is Nifty Call & Put Options?
Ans. The Nifty Call Option is the option contract of the Nifty 50 index with different strike prices. While the Nifty Put option is the option contract of the Nifty 50 index with different strike prices and various expiration dates trading on the stock exchange.
Q6. What is Nifty Option Lot Size?
Ans. The lot size of the Nifty option is 50 for any strike price. This means anyone looking to buy or sell the Nifty 50 option contract to trade a minimum 50 market lot and further can buy or sell the Nifty 50 option contract in the multiple of 50 – like 100, 150, 200, and 250 so on.
Q7. What is the Bank Nifty Option Lot Size?
Ans. The market lot size of the Bank Nifty Option is 15 and a trader can buy or sell in the option market. Further, in the multiple 15, Bank Nifty Option can be bought and sold in the option market. Earlier it was 25, but in an effort to increase customer participation in the derivatives marketnowNSE has decreased the market lot size for Nifty Bank futures and Options.
Q8. What is Nifty Option Maximum Lot Size?
Ans. As per the latest updates the maximum number of lots per order in Nifty option can be placed at 36. This means in Nifty 50 option, anyone can buy or sell per order a maximum of 1800 units. The maximum units are calculated by multiplying the maximum lots per order i.e. 36 with the maximum lot per order.
Q9. Is Option Trading Profitable?
Ans. Options trading can be profitable only when you trade with the right option strategy. Never play a naked option game, always cover your position or you can trade in a long call in which the loss is limited and profit can be unlimited. In buying the Call option you will make a profit equal to the difference between the stock price and strike price minus the premium.
Q10. Is Option Trading Safe?
Ans. No option trading is not safe if you are a naked seller, which means if a buyer of option trading naked there is limited loss, but when a seller is selling a naked call, it is a risky game. Always make a covered position and use this as a hedging strategy to reduce the risk and enjoy a profitable trading journey.
Q11. What is a Naked Option Strategy?
Ans. In the naked option strategy, an option seller sells the call option on an asset that is not owned by him. This means if you write or sell a call option on the stock of XYZ Company that you actually don't have in your demat account.
Q12. What is a Covered Option Strategy?
Ans. In the covered option strategy, a seller has the assets at the time of selling the call option. This means, if you are selling the call option of XYZ Company, you already have the stock of XYZ Company at the time of selling the option.
Q13. What is a Covered Call?
Ans. A Covered Call is an option strategy, in which an investor sells the Call option on stock that is owned by him. Usually, in the covered call, Out-of-the-Money is sold, which means when the Call option strike price is more than the current market price of the underlying stock. The Call seller retains the premium for writing the call and it is the income of the call seller this strategy is usually adopted when you think the stock is moderately bullish and does not go beyond the strike price.
Q14. Is Option Premium Refundable?
Ans. No, not at all, once you paid the premium for buying an option contract, you cannot claim a refund in any situation. Most of the traders do not exercise the option contract, hence, it can be sold, bought and resold multiple times before the expiry date. Most traders buy options at a premium with the expectation to resell them later on at a higher premium depending on the change in the price of the underlying security.
Q15. Is Option Trading Legal in India?
Ans. Option trading or you can say Binary option trading is considered to be illegal in India but still traders perform option trading in the stock market and other tradable instruments. In fact, income from such speculative actions is liable to be taxed at a flat rate of 30%.
Q15. How to Read Nifty Option Chain?
Ans. When you open a Nifty Option chain window, you can see the table with particulars like strike prices, contract expiration date, option type (Call or Put) last trading prices of option call and put option, change in price, volume (contracts traded), open interest (OI) in each strike price and underlying security. All these data are shown in tabular format and you can open any option contract or strike price and check more details like top five bids and ask price and quantity, traded volume, traded value, market lot, change in OI and volatility – in daily, annualized and implied volatility.
Q16. What is the Nifty 50 Option Trading Time?
Ans. Just like the normal trading hours for the cash market, the trading hours in options or in the Derivatives segment on NSE and BSE are between 9:15 AM to 3:30 PM. All the options and futures trading can be performed during these trading hours and it is also known as a 'Continuous Trading Session'.
Q17. What is Nifty & Bank Nifty Option Expiry Date?
Ans. The expiry date of Nifty 50 and Bank Nifty future and options contracts is on the last Thursday of every month. If a holiday falls on the last Thursday then the contracts expire on the previous trading day.
Q18. How to Use Option Chain for Trading?
Ans. Anyone can choose the option chain to analyse the best strike price, as per the market sentiment or the trend in the underlying security to trade with a suitable option strategy and make profits.
Q19. What is the Risk in Options Trading?
Ans. Option trading is a highly risky game, as the premium prices of option contracts fluctuate with the price of the underlying security and are reduced with the time value of money. Options trading is a high-risk high-reward game, traders can incur huge losses if not traded with the right strategy.
Q20.How to Start Trading in Options in India?
Ans. To start trading in options just open a trading and demat account with Moneysukh, and provide all the details required for trading in the derivatives segment and anyone can start trading in options in India.
















No comment yet, add your voice below!