Bearish Strategies
Bear call spread
Setup of the strategy
- Sell 1 call at lower strike
- Buy 1 call at higher strike
The maximum loss is defined. The worst-case scenario at expiry is that the security price is greater than the higher strike. Such circumstances will lead to 2 cases. The lower put that was sold will be executed because it is now deeply in the money. The investor/trader will then execute the higher call to avoid further losses. A short call main purpose is to generate income. The profitability of the approach is assessed by how much of the premium revenue is retained until the option expires. The approach works best if the stock remains below the lower strike price during the option tenure. An unanticipated surge, on the other hand, should not be a problem: while the greatest gain of this approach is relatively limited, so are the probable losses.
In this strategy, the maximum loss is capped. At the time of expiry, the worst-case condition is that the underlying asset price surpasses the higher strike. In this case, the investor will sell the securities to the short-call holder before exercising the long call. The shares will be sold at the lower strike and purchased at the higher strike as a consequence of the simultaneous exercise. The max loss is equal to the difference between the two strikes, but it is reduced by the initial net credit.
The maximum profit is restricted to the net premium received. The security price at expiry might stand below both strike prices. Both call options expire worthless in this case, and the investor retains the credit gained when initiating the deal.
The investor’s choice of the two strike prices defines the maximum revenue potential and maximum risk. The investor can improve the first net premium income by picking a lower short call strike and/or a higher long call strike.
Breakeven = short call strike + net credit received
Let’s now take up a scenario to elaborate Bear Call option strategy.
Nifty is at 18485. BUY 18450 CALL AND SELL 18150 CALL
| Option Type | Expiry Date | Strike Price | LTP | Action | No. Of Lots |
| CALL | 29-12-2022 | 18200 | 545.4 | Sell | 1 |
| CALL | 29-12-2022 | 18500 | 327.55 | Buy | 1 |
Payoff detail
| Max Risk | Max Reward | Lower Break Even | Upper Break Even |
| 82.14996 | 217.85004 | 18417.85 | 18417.85 |
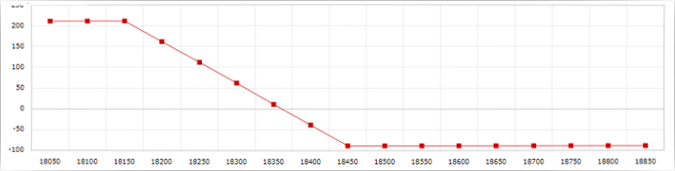
| Market Expiry | Payoff 1 | Payoff 2 | Net Premium | Option PayOff At Expiry |
| 18100 | 0 | 0 | 210 | 210 |
| 18150 | 0 | 0 | 210 | 210 |
| 18200 | 0 | 0 | 210 | 210 |
| 18250 | -50 | 0 | 210 | 160 |
| 18300 | -100 | 0 | 210 | 110 |
| 18350 | -150 | 0 | 210 | 60 |
| 18400 | -200 | 0 | 210 | 10 |
| 18450 | -250 | 0 | 210 | -40 |
| 18500 | -300 | 0 | 210 | -90 |
| 18550 | -350 | 50 | 210 | -90 |
| 18600 | -400 | 100 | 210 | -90 |
| 18650 | -450 | 150 | 210 | -90 |
| 18700 | -500 | 200 | 210 | -90 |
| 18750 | -550 | 250 | 210 | -90 |
| 18800 | -600 | 300 | 210 | -90 |
| 18850 | -650 | 350 | 210 | -90 |
| 18900 | -700 | 400 | 210 | -90 |
Bear put spread
Setup of the strategy
- Buy 1 ITM Put
- Sell 1 OTM Put
A bear put spread strategy is buying and selling options for the same underlying asset at different strikes for the same expiration date. The strategy is designed to be cost-effective. The bear put spread option strategy is established for a net cost. The strategy is used when trader believes that the underlying asset’s price will fall moderately in the near term.
When an investor or trader wants to profit on a little dip in the price of a security, this method is applied.
The options trader decreases the cost of initiating the strategy by shorting the out-of-the-money put, but foregoes the opportunity of generating a substantial return if the underlying security price falls. Because a debit is taken upon initiating the trade, it is also known as the bear put debit spread.
In order to reap the maximum gain, the security price must close below the strike price of the OTM puts at expiration. Both options expire ITM, but the higher strike put purchased has a larger intrinsic value than the lower strike put sold. As a result, the max profit from the bear put option strategy is the difference in strike price minus the debit is taken when the position was initiated. If the stock price rises above the ITM put strike at expiry, the bear put spread strategy will incur a maximum loss equal to the debit taken upon entering the trade.
Breakeven Point = Strike Price of Long Put – Net Premium Paid
Let’s now take up a scenario to elaborate Bear Put option strategy.
Nifty is at 18485. SELL 18150PUT AND BUY 18500 PUT.
| Option Type | Expiry Date | Strike Price | LTP | Action | No. Of Lots |
| PUT | 29-12-2022 | 18150 | 106.75 | Sell | 1 |
| PUT | 29-12-2022 | 18500 | 205.1 | Buy | 1 |
Payoff Details
| Max Risk | Max Reward | Lower Break Even | Upper Break Even |
| 98.350006 | 251.65 | 18401.65 | 18401.65 |
| Market Expiry | Payoff 1 | Payoff 2 | Net Premium | Option PayOff At Expiry |
| 18100 | -50 | 400 | -98.35 | 251.65 |
| 18150 | 0 | 350 | -98.35 | 251.65 |
| 18200 | 0 | 300 | -98.35 | 201.65 |
| 18250 | 0 | 250 | -98.35 | 151.65 |
| 18300 | 0 | 200 | -98.35 | 101.65 |
| 18350 | 0 | 150 | -98.35 | 51.65 |
| 18400 | 0 | 100 | -98.35 | 1.65 |
| 18450 | 0 | 50 | -98.35 | -48.35 |
| 18500 | 0 | 0 | -98.35 | -98.35 |
| 18550 | 0 | 0 | -98.35 | -98.35 |
| 18600 | 0 | 0 | -98.35 | -98.35 |
| 18650 | 0 | 0 | -98.35 | -98.35 |
| 18700 | 0 | 0 | -98.35 | -98.35 |
| 18750 | 0 | 0 | -98.35 | -98.35 |
| 18800 | 0 | 0 | -98.35 | -98.35 |
| 18850 | 0 | 0 | -98.35 | -98.35 |
| 18900 | 0 | 0 | -98.35 | -98.35 |

Synthetics
Synthetics are a method of creating an artificial financial position using a different technique. Derivatives enable investors to build multiple positions synthetically without having to utilise as much capital. Using options, there are numerous methods to generate synthetic positions. One of the benefits of having this synthetic position in security rather than possessing the security is that it is less expensive than holding the security outright. The options position might provide us with up to double the leverage of holding the stock overnight. This may allow us to enhance the return on the portfolio.
Synthetic short stock
The synthetic short stock strategy is an options strategy that mimics the reward of shorting a stock position. An investor/trader can establish a synthetic short stock position instead of actively shorting a stock. Traders construct such a strategy by buying at-the-money (ATM) put and selling an equal number of at-the-money (ATM) calls with the same expiration date.
Setup of the strategy
- Buy 1 ATM Put
- Sell 1 ATM Call
Profit is made in this strategy when the underlying stock’s price trades below the strike price of the purchased long put options during the life of an option. The profit is equal to the profit from the long put options, plus the revenues from the sale of call options, less the premiums paid for buying the put options and any transaction fees.
The synthetic short stock strategy is a two-edged sword in that it entails an endless amount of risk while the potential of providing a huge reward. The worst-case scenario is that the security continues to rise, forcing the call seller to deliver the shares at the strike price, suffering an infinitely large loss. The risk/reward profile is nearly identical to short stock. The highest profit is significant yet restricted. The worst-case scenario that may happen is that the stock loses much of its value, in which case the investor can purchase shares at a bargain from the market and sell it at the strike price by executing the put.
Let’s now take up a scenario to elaborate Synthetic short stock option strategy.
NIFTY is trading at 18486. BUY 18500 PUT AND SELL 18500 CALL.
| Option Type | Expiry Date | Strike Price | LTP | Action | No. Of Lots |
| PUT | 29-12-2022 | 18500 | 202.1 | Buy | 1 |
| CALL | 29-12-2022 | 18500 | 327 | Sell | 1 |
Payoff detail
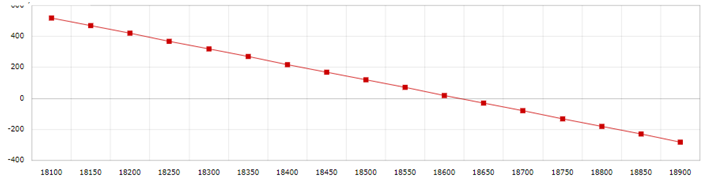
| Market Expiry | Payoff 1 | Payoff 2 | Net Premium | Option PayOff At Expiry |
| 18100 | 400 | 0 | 124.9 | 524.9 |
| 18150 | 350 | 0 | 124.9 | 474.9 |
| 18200 | 300 | 0 | 124.9 | 424.9 |
| 18250 | 250 | 0 | 124.9 | 374.9 |
| 18300 | 200 | 0 | 124.9 | 324.9 |
| 18350 | 150 | 0 | 124.9 | 274.9 |
| 18400 | 100 | 0 | 124.9 | 224.9 |
| 18450 | 50 | 0 | 124.9 | 174.9 |
| 18500 | 0 | 0 | 124.9 | 124.9 |
| 18550 | 0 | -50 | 124.9 | 74.9 |
| 18600 | 0 | -100 | 124.9 | 24.9 |
| 18650 | 0 | -150 | 124.9 | -25.1 |
| 18700 | 0 | -200 | 124.9 | -75.1 |
| 18750 | 0 | -250 | 124.9 | -125.1 |
| 18800 | 0 | -300 | 124.9 | -175.1 |
| 18850 | 0 | -350 | 124.9 | -225.1 |
| 18900 | 0 | -400 | 124.9 | -275.1 |
Neutral Strategies
Neutral Options Strategies are options strategies that profit when the underlying stock remains constant or within a predetermined price range. There are no other financial instruments that allow a trader to profit when a stock is completely still. There are numerous neutral strategies available, including the straddle, butterfly, strangle, condor, and so on.
An investor/trader can advantage from neutral strategies by three ways
- You will profit even if the underlying security does not move at all.
- Whether the underlying security’s price rises or falls, you will still profit as long as the price movements remain within an acceptable range.
Short straddle
Setup of the strategy
- Short call
- Short put
The long straddle approach is the inverse of the short straddle strategy. A short straddle is a strategy that combines one short call and one short put option with the same strike, underlying asset, and expiration date. When the underlying security price trades in a narrow range around the strike price, the technique is profitable. During the life of the options, the strategy predicts a steady stock price. As a consequence, “neutral or sideways” is the best forecast. This strategy is deployed for a net credit.
When the underlying stock’s price trades in a narrow range around the strike price, the technique is successful. During the life of the options, the strategy predicts a constant stock price. As a consequence, “neutral or sideways” is the best forecast. For a net credit, a short straddle is used.
Profitability is limited to the total credit premiums minus all taxes and regulatory expenses. If the short straddle is held to expiry, the stock price remains and closes in a narrow range to the strike price, and both options expire worthless, the maximum profit is obtained.
If the security price at expiry equals the strike price of a short straddle, both the call and put option expire worthless, and no stock position is established.
If the security’s price at expiry surpasses the strike price, the put option loses value while the short call is exercised. The exercise results in the sale of the shares at the strike price, creating a short stock position.
The call option expires worthless if the security’s price at expiry is less than the strike price, but the short put option is exercised. The exercise results in the purchase of shares at the strike price, resulting in a long position in an underlying security.
If the stock price rises, the potential loss is infinite. If the stock price drops, the loss is substantial but restricted until the price goes to zero.
Let’s now take up a scenario to elaborate Short Straddle option strategy.
NIFTY is trading at 18468. SELL 18450 PUT AND SELL 18450 CALL
| Option Type | Expiry Date | Strike Price | LTP | Action | No. Of Lots |
| PUT | 29-12-2022 | 18450 | 178 | Sell | 1 |
| CALL | 29-12-2022 | 18450 | 376.3 | Sell | 1 |
Payoff detail
| Max Risk | Max Reward | Lower Break Even | Upper Break Even |
| Unlimited | 554.3 | 17895.7 | 19004.3 |
| Market Expiry | Payoff 1 | Payoff 2 | Net Premium | Option PayOff At Expiry |
| 18050 | -400 | 0 | 554.3 | 154.3 |
| 18100 | -350 | 0 | 554.3 | 204.3 |
| 18150 | -300 | 0 | 554.3 | 254.3 |
| 18200 | -250 | 0 | 554.3 | 304.3 |
| 18250 | -200 | 0 | 554.3 | 354.3 |
| 18300 | -150 | 0 | 554.3 | 404.3 |
| 18350 | -100 | 0 | 554.3 | 454.3 |
| 18400 | -50 | 0 | 554.3 | 504.3 |
| 18450 | 0 | 0 | 554.3 | 554.3 |
| 18500 | 0 | -50 | 554.3 | 504.3 |
| 18550 | 0 | -100 | 554.3 | 454.3 |
| 18600 | 0 | -150 | 554.3 | 404.3 |
| 18650 | 0 | -200 | 554.3 | 354.3 |
| 18700 | 0 | -250 | 554.3 | 304.3 |
| 18750 | 0 | -300 | 554.3 | 254.3 |
| 18800 | 0 | -350 | 554.3 | 204.3 |
| 18850 | 0 | -400 | 554.3 | 154.3 |

Short strangle
Setup of the strategy
- Sell 1 call at higher level
- Sell 1 put at lower levels
A short strangle strategy is employed for a net credit. A trader/investor sees this strategy lucrative if he sees underlying security to trade inside a narrow range between the break-even points. Profitability is limited to the total premiums paid less commissions. The Short Strangle is a risk-free technique that employs out-of-the-money Call and Out-of-the-money Put options. Put alternatives. Put options with the same underlying asset and expiration date are sold together.
Profitability is restricted to the total premiums received in the employment of the strategy, less any commissions. If the underlying security price closes at or between the strike, and both options expire worthless, max profit is earned. The underlying security price might continue to climb indefinitely, and the potential loss to the upside is limitless. On the flip side, the potential loss is significant because the security price might go to zero.
If the underlying asset is trading in a very tight range to the strike prices at the time of expiration, both the call and put options expire worthless, and no position is established.
Also read Bullish option Strategies
If the security price at expiry exceeds the strike price of the call option, the put option expires worthless and the short call option is exercised. The underlying asset is sold at a strike price that is lower than the market price, leading in the creation of a security short position.
If the security price at expiry is less than the put option’s strike price, the call option loses value and the short put option is exercised. The securities are purchased at a higher strike price than the market price, and a long position is created.
Let’s now take up a scenario to elaborate Short strangle option strategy.
NIFTY is trading at 18512. SELL 18550 CALL AND SELL 18450PUT.
| Option Type | Expiry Date | Strike Price | LTP | Action | No. Of Lots |
| CALL | 29-12-2022 | 18550 | 300.75 | Sell | 1 |
| PUT | 29-12-2022 | 18450 | 180.5 | Sell | 1 |
Payoff details
| Max Risk | Max Reward | Lower Break Even | Upper Break Even |
| Unlimited | 481.25 | 17968.75 | 19031.3 |
Also read Neutral Options Strategies
| Market Expiry | Payoff 1 | Payoff 2 | Net Premium | Option PayOff At Expiry |
| 18100 | 0 | -350 | 481.25 | 131.25 |
| 18150 | 0 | -300 | 481.25 | 181.25 |
| 18200 | 0 | -250 | 481.25 | 231.25 |
| 18250 | 0 | -200 | 481.25 | 281.25 |
| 18300 | 0 | -150 | 481.25 | 331.25 |
| 18350 | 0 | -100 | 481.25 | 381.25 |
| 18400 | 0 | -50 | 481.25 | 431.25 |
| 18450 | 0 | 0 | 481.25 | 481.25 |
| 18500 | 0 | 0 | 481.25 | 481.25 |
| 18550 | 0 | 0 | 481.25 | 481.25 |
| 18600 | -50 | 0 | 481.25 | 431.25 |
| 18650 | -100 | 0 | 481.25 | 381.25 |
| 18700 | -150 | 0 | 481.25 | 331.25 |
| 18750 | -200 | 0 | 481.25 | 281.25 |
| 18800 | -250 | 0 | 481.25 | 231.25 |
| 18850 | -300 | 0 | 481.25 | 181.25 |
| 18900 | -350 | 0 | 481.25 | 131.25 |


















No comment yet, add your voice below!