On Friday RBI made a big change related to interest rates by cutting down the repo rate from 25 basis points after a stagnant rate of 6.50% for 2 years. This decision comes after RBI’s six members Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) lowered the interest rate to boost economic activities and growth, lowering down in the interest of equated monthly installments (EMIs), and easy lending for home and personal loans while managing the inflation rate in the country. It is an important decision by RBI when the world is going through economic instability and tariffs fear by the U.S. makes the situation more serious. To increase the GDP growth rate and employment opportunity in the economy RBI reduced its interest rate; RBI estimated the GDP growth rate at 6.7% and retail inflation projection at 4.2% for the fiscal year 2025-26.
Repo rate refers to the rate at which RBI lend money to commercial bank in country. This rate directly influences the economic activity level, investment and saving rate of people in country.
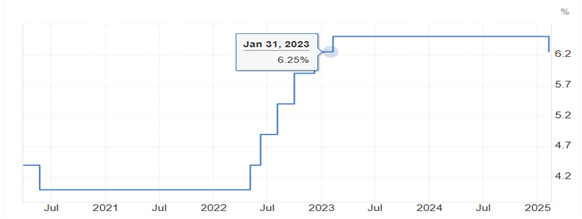
Interest Rate Change by RBI
But why did RBI cut the repo rate in the economy?
The primary reason to cut down the repo rate is to stimulate in growth of the economy through cheap availability for borrowing for individuals and businesses which leads to increased spending and investment. This rate cut helps banks to reduce their interest rate of loans to people which creates more income and saving rates for individuals which leads to more demand and expenditure, in short boosting economic growth. A higher rate of spending and investment directly supports more opportunities for job creation and employment. Although inflation is within the control of the RBI range, a rate cut can help support growth and maintain price stability. The rate decision of RBI helps India to align with global economic trends, as data shows that many central banks adopted accommodative monetary policies.
How it will impact the economy?
RBI’s decision to lower down interest rate will affect the economy in a positive way because lower rate availability of interest rates on loans by commercial banks to individuals and businesses increases spending and investment rates in the economy which helps in the GDP growth rate and improves other conditions that are stagnant. Individuals and businesses both will benefit because lower interest rates encourage them to more expenditure and investment respectively.
A lower interest rate makes the equity market more attractive because investors expect better returns because lower interest in the economy encourages individuals to spend more money in consumption which directly increases the demand & profits margin of companies. The lower interest rate makes the bond market less attractive because people are getting better returns from the equity market, this encourages individuals to invest more in equity rather than the bond market. But it will also give an indication to investors that the economy is in slow down which might make investors cautious.
Lower interest rate affects positively on banks and financial institutions because banks usually borrow money from RBI and if rates are lower down by RBI banks will follow the same, if banks not follow the interest rate of RBI could affect their profits. But if the banks follow the rate cuts of RBI this will lead to increase in demand of loan in people which will increase the profits of banks and financial institutions.
RBI’s decision to cut down the repo rate from 25 basis points affects largely and in a positive manner for home loans and EMIs which help households to increase in income because when the money is lent by RBI to commercial banks at a lower rate this will encourage banks to lower down the interest rate of home loans, personal loans, etc. It will increase the number of loans taken by households. It also reduces the rate of EMIs by banks due to the lower rate of money lent by RBI to banks which reduces the cost of interest borrowing funds and will encourage banks to cheaper lending in the market. The change in lower interest will also help the existing borrower in debt relief because now they can pay their interest to the bank at a lesser rate as compared to the previous rate. RBI’s decision will definitely give a direct boost to the housing sector because of low interest rate on home loans encourages individuals in the economy to take more loans for acquiring new land or home but along with it this will also down the interest rate which we receive on our saving account in bank because bank have better availability of fund for their working from RBI, same effects will also seen in the fixed deposits (FD) interest rates which discourage individual to save money in banks.
Stocks and Sectors in focus after rate cut:
Financial and NBFCs
After RBI decision financial sector and NBFCs will directly affected positively because liquidity condition improve by lower interest. The availability of cheap credit encourage banks to lend more money to individual and businesses, this will improve business operations of banks and NBFCs often raise their money from bonds and debenture, in this rate cuts increase better opportunities in market.
FMCG and Durable goods
As RBI supports more liquidity in the market through rate cuts, it will encourage individuals in the market to spend more money on consumption because for the past two years consumption rate has been lagging and rate cuts affect it positively.
Real Estate
Lower interest for commercial banks stimulate to provide further loan to people at lower rate. As people have option of lower interest rate they will take loan and invest in buying home for their living which will boost demand in real estate.
The Flip Side of low interest rates
RBI rate cuts not only affect the economy in a positive way but there is also down side of this decision. RBI rates cut can spike the inflation rate as more money comes into the hands of individuals they start demanding more products and increasing their expenditure which will lead to a rise in the inflation rate, but currently inflation is in the RBI range. Lower rate give accessibility of money to commercial banks which made easy availability of funds to common people at lower rate make currency weaker because as inflation rises higher the value of the currency falls which depreciates domestic currency in the market and leads to higher costs for import & makes domestic market unattractive for foreign investors.