Long Call Option Strategy-Bullish Options Trading Strategies
Long call option trading strategy is one of the basic trading approaches that involve buying options, to be precise buying call option. Implementation of the strategy involves going long on a call option. The trader/investor is optimistic in the short term and wants to participate in the security’s upside during the option’s term. If the market/underlying rises as per the expectation of the call holder, the trader can then benefit by selling the call at a profit.
Risk in Long Call Option Trading
When the trader holds on to the contract till the expiry and the underlying asset price trades below the intended price of the call option for buyer, the maximum loss is restricted to the premium paid for getting long on the call option. When the security price falls below the contract price, the contract becomes useless and the premium paid is forfeited.
Reward
Being on the right side of a turbulent market can quickly transform a stock in to a multi bagger. Similarly, an underlying can potentially ascend to infinite. In that scenario, the trader could either sell the option at extreme gain or exercise the contract and buy the stock at the predetermined strike price.
Break-Even Point
Breakeven point for Long Call Option Strategy is determined when the stock price equals the strike price plus the premium spent to acquire the call option at the time of expiration. Any rise in the stock price above the strike price results in a positive upside in profit.
Breakeven = Strike Price + Premium Paid
Construction of Long Call Option Strategy
Buy 1 Call option
| Option Type | Expiry Date | Strike Price | LTP | Action | No. Of Lots |
| CALL | 29/03/2023 | 17000.0 | 209.35 | Buy | 1 |
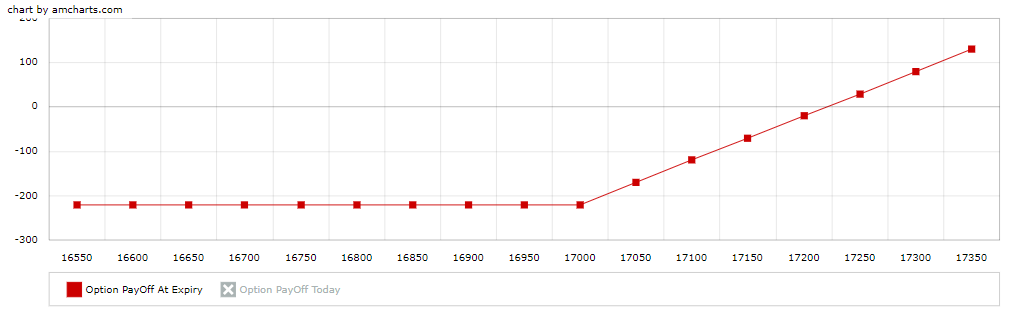
Payoff Chart
| Market Expiry | Payoff 1 | Net Premium | Option PayOffAt Expiry |
| 16550.0 | 0.0 | -209.35 | -209.35 |
| 16600.0 | 0.0 | -209.35 | -209.35 |
| 16650.0 | 0.0 | -209.35 | -209.35 |
| 16700.0 | 0.0 | -209.35 | -209.35 |
| 16750.0 | 0.0 | -209.35 | -209.35 |
| 16800.0 | 0.0 | -209.35 | -209.35 |
| 16850.0 | 0.0 | -209.35 | -209.35 |
| 16900.0 | 0.0 | -209.35 | -209.35 |
| 16950.0 | 0.0 | -209.35 | -209.35 |
| 17000.0 | 0.0 | -209.35 | -209.35 |
| 17050.0 | 50.0 | -209.35 | -159.35 |
| 17100.0 | 100.0 | -209.35 | -109.35 |
| 17150.0 | 150.0 | -209.35 | -59.35 |
| 17200.0 | 200.0 | -209.35 | -9.35 |
| 17250.0 | 250.0 | -209.35 | 40.65 |
| 17300.0 | 300.0 | -209.35 | 90.65 |
| 17350.0 | 350.0 | -209.35 | 140.65 |
Option Trading Example
NIFTY is trading around 17000 levels, and a trader takes a bullish perspective on the market and purchases one 17000 In-the-money Call Option for a premium of Rs. 230.
Scenario 1: The NIFTY ends at 17300, and the trader will exercise the long call option and makes a profit of Rs. 15000 at the contract level. [(17300-17000)*50]
Scenario 2: The NIFTY falls to 16850 levels; because the right to purchase is greater than the market price, the trader will let option expire worthless. The trader will suffer a loss at the contract level of Rs. 11500 (230*50), which is the premium paid for buying call option @17000 strike.
Scenario 3: If the benchmark ends not above or below but at the target price of the long call option, the investor will lose the premium paid to purchase the call option.
All Moneysukh clients can make their option trading strategies by logging on to Traderadat.moneysukh.com and that for no charges.
Also read: Synthetic Long Call option strategy


















No comment yet, add your voice below!