How to read financial documents
In India, the list of financial statements and its format that listed companies need to maintain and publish are governed by Schedule III of the Companies Act 2013 and IndAS ( Indian Accounting standard)
As per IndAS1, an absolute set of financial statements that listed companies necessitate to make public include the following:
(i) Balance sheet: It provides information on the financial/monitory position i.e. assets, liabilities, and equity at the end of the financial reporting period.
(ii) Statement of profit and loss account: It gives data around the company’s financial execution i.e. income, expense and profits ,salary, cost and benefits for a given period. . It is also referred to as profit and loss account. IndAS 1 requires the statement to also include
other comprehensive income (OCI) - OCI includes certain gains or losses on account of changes in fair value of assets and liabilities that are required/permitted to be not recognized as part of income and expense.
(iii) Statement of changes in shareholder's equity: Shareholder’s value alludes to the funds that have a place to the shareholders. It can experience alter on account of different factors profits earned, dividends paid, additional shares issued, buy back and certain income and certain income and other comprehensive income. IndAS 1 recognizes this statement as part of balance sheet.
(iv) Cash flow statement: Cash flow statement provides a summary of the various sources and uses of cash.
(iv) Detailed notes explain the accounting policy and break down of information presented in the financial statement.
In India, the list of financial statements and its format that listed companies need to maintain and publish are governed by Schedule III of the Companies Act 2013 and IndAS ( Indian Accounting standard)
As per IndAS1, an absolute set of financial statements that listed companies necessitate to make public include the following:

Whereas displaying the financial data, companies will got to give comparable information for at slightest one earlier period. Hence, each budgetary explanation ought to contain information for the current period and the earlier period. Companies can unveil or provide comparative financials for a longer period, in the event that they prefer. One of the key departing features of financial statement regulation in India compared to rest of the world is that, in India, financial statements are expected to be meant for general purpose. It is anticipated to serve distinctive sorts of audience including shareholders, lenders, employees / trade unions, government, vendors and general public. On the other hand, many other countries insist the financial statements are targeted at their investors
Stand alone financial statement and consolidated financial statement
Within the eyes of law every company may be a isolated enlisted substance. Be that as it may, regularly we moreover come across circumstance where a company is possessed and controlled by another company. For example, Jio Platforms is a separate company, but it is majority owned and controlled by Reliance Industries Limited. Similarly, Toyota Kirloskar Motor Limited is majority owned by Toyota Motor Corporation, Japan. Since each company is a separate registered entity, each company prepares its own individual financial statement (referred as stand-alone financial statement). However, in case of large groups, these stand-alone financial statements can prove quite misleading. For instance, Toyota Motor Corporation is a Japanese company, but it operates across the world through several of its subsidiary companies. If we look at the stand-alone financial statement of Toyota Motor corporation, it would only show sales of that independent entity i.e., sales in Japan. Thus, sales of Toyota group in rest of the world including China, India or North America or any other part of the world done through the subsidiary will not reflect in their sales.
Therefore, companies are required to present consolidated financial statement. In consolidated financial explanation, all companies that are controlled by a company are treated as portion of a single gather. In this way, it combines the budgetary execution of all the gather companies together and presents it as portion of a single money related articulation. SEBI directions require recorded companies to distribute solidified monetary articulations on an yearly premise. Advance, it too commands recorded companies to distribute stand-alone budgetary comes about on a quarterly premise. Indeed in spite of the fact that it isn't required, a few companies intentionally distribute their solidified budgetary explanation on quarterly basis.
Common Balance Sheet Line Items
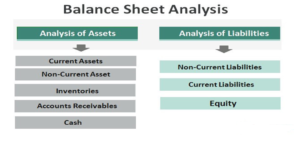
Assets: Assets speaks to things that are anticipated to supply future benefits. Be that as it may, as per the by and large acknowledged bookkeeping standards, a company can recognize as it were those resources which are quantifiable in money related terms and have been paid for. In common, an substance cannot recognize self-generated resources such as claim brand name. The assets of a company are classified into current assets and non-current assets: a) Non-current resource speaks to resources that are likely to allow benefits over the long term. In general, all resources other than current resources (clarified underneath) are non-current assets. b) Current asset speaks to resources that are likely to advantage the organization inside one operating cycle. In most cases, the residency of the working cycle is taken as one year.
Non current assets
Property, Plant and Equipment (PPE): These include assets such land, building, machineries, furniture, computers and other similar items. These assets are shown at historical cost (net of accumulated depreciation). IndAS 16 allows a company to use a revaluation-based model, where the assets are periodically revalued and shown at revised value. The choice to apply revaluation method should be applied for an entire asset class. In the above exhibit, the value of PPE as on 31-Mar-2019 was Rs.815.2 billion.
Capital work in progress: These represent PPE that are currently under construction i.e. not ready for operation. When the assets are completed and are ready for operation, it is transferred to PPE.
Goodwill: Goodwill arises when a company acquires another business. It represents the amount of consideration paid by a company over and above the fair value of net assets taken over. For example, in FY 2018, Bharti Airtel acquired 100% stake in Tigo Rwanda Ltd for Rs.3,200 crores. However, the fair value of net assets of Tigo (assets – liability) was only Rs.2,838 crores. The balance was recognized as goodwill. Goodwill is generally considered as a fictitious asset as it cannot be sold independently. It is periodically tested for impairment and if its value in use is lower than its carrying value, the difference is written off as impairment. In case if a company pays an amount lower than the fair value of asset taken over, that difference is taken to capital reserves.
Intangible assets: Intangible assets refer to assets that are generally in the form of a legal right. Acquired copy rights, patents and brand names are some examples of intangible assets. It is important to note that self-generated assets cannot be shown in the balance sheet. However, internally developed software programs can be recognized as asset. These assets are generally shown at cost minus accumulated amortisation.
Current Assets:
Inventory: Inventory includes the value of raw material, work-in-progress, and unsold finished goods at the end of the reporting period. These are shown at cost price or market value, whichever is lower.
Current Financial assets: These represent cash, cash equivalents, bank balances, short term investments, receivables and other financial claims that are likely to be received within one year.
- Cash and cash equivalents: It includes cash, balances in current accounts, short-term bank deposits and money market investments.
- Bank balance: Includes balances in all bank accounts other than those included in cash equivalents.
- Receivables: Represents amount receivable from customers. They are shown net off provision for doubtful debts.
- Investments: Represent value of short-term investments and are shown at fair market value.
- Others: Any other claim that is likely to be received within one year.
Other current assets: Represents other assets that are likely to provide benefits within the next one year. These include prepaid expenses or any such assets where the benefit is likely to be received in kind i.e., as goods or service rather than as cash or equivalents.
Liabilities
Equity: Equity speaks to the leftover intrigued in a company, which has a place to the proprietors of the company. It represents the value of assets minus liability. It has several sub-components. The breakdown is not necessarily of significant concern to financial analysts on most occasions.
Share capital: Represents the face value of the paid up share capital of the company
Share premium: Represents the amount received towards paid up capital that is over and above the value of shares.
Retained earnings: Refers to the total amount of profit and other comprehensive income earned by a company that has not been distributed as dividend or set aside for any other purpose.
General reserve: Represents the part of retained earnings which a company has set aside for utilising in future for any specific purpose.
Non-current liabilities: It represents obligations of the company that have been fulfilled after one year. There are numerous liabilities that drop beneath this category.
Long Term Debt: Represents amount repayable towards borrowings, in the form of loans, or in the form of debentures/bonds/notes that are due beyond one year. Some portion of the long term may fall due within one year. Such portion of long term debt is shown separately as current portion of long term debt.
Provisions: Provision represents amount set aside for a liability which is yet to be fully quantified. Unlike reserves, which are set aside for unknown purpose, provisions are amount set aside to meet a specific obligation. However, company may not be able to fully quantify it. The most common example is provision for retirement benefit obligation payable to their
employees at the time of their retirement. Other illustrations incorporate arrangement towards warranty obligations, arrangement towards lawful risk that's however to be settled. Provisions towards obligations that got to be met past one year are included beneath non-current liability.
Current Liabilities: It speaks to commitments of a company that it has to satisfy inside one year. A company has a few commitments that got to be performed inside one year.
Payables: It speaks to that sum payable to providers of products and administrations.
Short-term debt: Short term obligation are those that are borrowed for a period less than one year. Although, hypothetically, short-term obligations are due inside one year, numerous of the short-term debts are ordinarily rolled over or renegotiated. Hence, companies tend to carry their short-term debts longer into the future.
A few of the other current liability for a company incorporates the following: (i) Short term provisions
(ii) Current portion of long-term liability
(iii) Deferred revenue
(iv) Advances from customers
(v) Unpaid expenses and expense accrued but not due
Analyze your favorite stocks with Moneysukh
Contributing in stocks can be fulfilling once you investigate the issuing companies completely. Gone are the days when data was blocked off. With the advent of the our Mobile app and web platform, you have got all the data you wish about a company, like its income stream, items, financials, and other information, at your fingertips. Utilizing this, you'll dissect the specified stock in detail to evaluate whether it may be a practical venture or not.
Beneath the financials, any investor looks at financial ratios and financial explanations such as the profit and loss statement, the balance sheet, and money stream articulation that recommend how the company has performed so distant and clues at how it can passage within the future. You can find all such details on Moneysukh Stock Pages, which host comprehensive details about a company’s financials, peers, key metrics, and more.














2 Comments
[…] Also Read: How to Read Financial Documents […]
[…] Also Read:How to Read Financial Documents […]